1. How to Set Up Your First Google Ads Campaign
Setting up a Google Ads campaign is a structured process that involves defining goals, selecting keywords, creating ads, and optimizing for performance. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
Step 1: Define Your Campaign Goals
- Start by defining what you want to achieve with Google Ads: increasing website traffic, boosting conversions, raising brand awareness, or something else.
Step 2: Choose Your Campaign Type
- Google Ads offers different campaign types, including Search, Display, Shopping, and Video. The right campaign depends on your goals. For instance, Search Ads target user searches, while Display Ads appear across Google’s partner websites.
Step 3: Set Up Your Campaign
- Define your budget, bidding strategy (e.g., Cost-per-Click, Cost-per-Thousand Impressions), and targeting options (location, language, device).
Step 4: Conduct Keyword Research
- Use Google’s Keyword Planner Tool to find relevant keywords for your business. Focus on high-intent keywords that are most likely to lead to conversions.
Step 5: Write Your Ad Copy
- Craft engaging headlines and descriptions that resonate with your target audience. Include a clear Call to Action (CTA) and make sure your ad copy is aligned with user intent.
Step 6: Set Up Your Landing Pages
- The landing page must match the ad’s promise, offering a seamless experience. This can improve your Quality Score, which is a factor in how much you’ll pay per click.
Step 7: Monitor and Optimize Your Campaign
- After launching your campaign, track metrics like Click-Through Rate (CTR), conversion rate, and Cost per Acquisition (CPA). Use A/B testing to experiment with different ad copy and bidding strategies.
Step 8: Scale Up Your Campaign
- Once you find what works, gradually increase your budget and expand your keyword set. Always monitor your return on investment (ROI).
2. Facebook Ads for Beginners: A Complete Walkthrough
Facebook Ads are a powerful tool for targeting specific audiences based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and location. Here’s how to get started:
Step 1: Set Up a Facebook Business Manager Account
- This is where you manage your ads, pages, and other assets. Set up your Facebook Business Page if you don’t have one.
Step 2: Define Your Objectives
- Facebook Ads allow you to choose from multiple objectives like Brand Awareness, Traffic, Engagement, Conversions, or Lead Generation. Choose one that matches your business goals.
Step 3: Identify Your Target Audience
- Use Facebook’s powerful targeting tools to hone in on your audience. You can target by location, age, gender, interests, behaviors, and more.
Step 4: Choose Your Ad Format
- Facebook offers several ad formats: Carousel (multiple images or videos), Single Image or Video, Slideshow, and Collection. Choose the format that best represents your offering.
Step 5: Set Your Budget and Schedule
- You can choose between a daily budget or lifetime budget and decide whether your campaign runs continuously or within a specified time frame.
Step 6: Craft Your Ad Creative
- Design your ad with high-quality images or videos. Write compelling copy with a strong CTA. Remember that your visuals and text should work together to grab attention.
Step 7: Launch and Monitor Performance
- Launch your campaign and use Facebook Ads Manager to track performance. Focus on metrics like CTR, conversion rates, and Cost per Lead.
Step 8: Optimize and Scale
- Experiment with different ad creatives, audience segments, and bidding strategies. Once you find a winning combination, scale your budget to reach more potential customers.
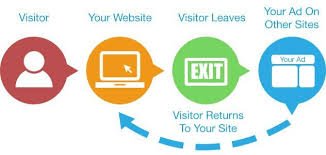
3. Retargeting Ads: What They Are and Why You Need Them
Retargeting (or remarketing) ads are a powerful tool that allows advertisers to target users who have previously interacted with their brand, but haven’t yet converted. Here’s why and how to use them:
What Are Retargeting Ads?
- Retargeting ads follow users around the internet after they visit your website, social media, or engage with your app. These ads encourage users to return to complete a purchase or take another desired action.
Why You Need Retargeting Ads
- Higher Conversion Rates: Users who have already shown interest in your products or services are more likely to convert on subsequent visits.
- Brand Recall: Retargeting helps increase brand recall by keeping your business visible to users over time.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Since you are targeting users who have already expressed interest, retargeting is typically more affordable than targeting cold prospects.
How to Set Up Retargeting Ads
- Install a Tracking Pixel: Add a Facebook Pixel or Google Remarketing tag to your website to track visitor behavior.
- Segment Your Audience: Create audience segments based on user activity, such as people who visited a specific product page but didn’t purchase.
- Create Compelling Ads: Tailor your ad copy and creative to users’ previous interactions, offering discounts, reminders, or showcasing the products they viewed.
- Monitor and Adjust: Track the performance of your retargeting campaigns and optimize your ads based on click-through rates, conversion rates, and ROI.
4. How to Optimize Your Google Ads for Higher ROI
Optimizing Google Ads for a better return on investment (ROI) requires a mix of smart strategies, constant monitoring, and adjustments. Here are the key steps:
1. Improve Your Quality Score
- Google uses a Quality Score to determine how relevant your ads are to the users’ search queries. A higher Quality Score can reduce your cost-per-click and improve your ad position. Key factors include:
- Ad Relevance: Ensure that your ad copy aligns with the keywords you are bidding on.
- Landing Page Experience: The landing page should be relevant, fast-loading, and mobile-friendly.
- CTR: Ads with higher click-through rates are seen as more relevant by Google.
2. Use Negative Keywords
- Exclude irrelevant keywords by adding negative keywords to your campaign. This prevents your ads from showing for irrelevant searches and helps save your ad budget.
3. Refine Your Targeting
- Narrow down your targeting to reach only the most relevant audience. Use geographic targeting, demographic targeting, and device targeting to ensure your ads are seen by potential customers.
4. Test and Optimize Ads
- Use A/B testing to determine which ad copy and creative work best. Test headlines, descriptions, CTAs, and landing pages. Constant optimization can lead to significant improvements in performance.
5. Monitor Your Bidding Strategy
- Choose the right bidding strategy based on your goals, whether that’s maximizing conversions or clicks. Experiment with automated bidding strategies like Target CPA or Target ROAS for more control over cost efficiency.
6. Leverage Ad Extensions
- Ad extensions like sitelinks, callouts, and structured snippets provide more information in your ads and improve their visibility, which can lead to higher CTR.
5. Should You Use Bing Ads? A Marketer’s Perspective
Bing Ads (now Microsoft Ads) are often overlooked in favor of Google Ads, but they can offer advantages, especially for certain audiences. Here’s a marketer’s perspective on whether to use Bing Ads:
Pros of Bing Ads
- Lower CPC: Bing Ads tend to have lower cost-per-click rates compared to Google Ads, making it a more cost-effective option.
- Less Competition: Since fewer advertisers use Bing, there is often less competition for keywords, leading to lower ad costs.
- Access to Microsoft’s Audience: Bing Ads reach users across the Microsoft network, including Windows, Xbox, Outlook, and others. This can be especially useful for targeting older, professional, or high-income individuals who are more likely to use Microsoft products.
Cons of Bing Ads
- Smaller Audience: Bing’s search engine market share is smaller than Google’s, so the reach of your campaigns might be more limited.
- Less Sophisticated Tools: While Bing Ads has made significant improvements, it doesn’t yet have the same range of tools and integrations as Google Ads.
When Should You Use Bing Ads?
- If you want to diversify your advertising strategy or if your target audience uses Microsoft products, Bing Ads could be a valuable addition. It’s also a good choice for businesses with smaller budgets looking to compete with lower CPCs.
These summaries give a comprehensive look at the essential points of each topic. For more detailed exploration, you can delve deeper into each subject, exploring tools, case studies, and advanced strategies.
1. How to Set Up Your First Google Ads Campaign
Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords) is a powerful tool that enables businesses to create and run ads on Google’s search engine and its vast network of websites. Setting up your first Google Ads campaign requires careful planning, execution, and continuous optimization to ensure the best results. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how to set up a Google Ads campaign from start to finish.
Step 1: Define Your Campaign Goals
Before diving into Google Ads, the first thing you must do is define your campaign objectives. Understanding your goals is crucial because it will guide all your decisions moving forward. Campaign goals could include:
- Increasing Website Traffic: Focus on driving more visitors to your site.
- Boosting Conversions: Encourage users to take specific actions (e.g., purchase, sign-up).
- Raising Brand Awareness: Create awareness and exposure for your brand.
- Lead Generation: Capture potential customer information for follow-up.
Understanding these objectives will also influence the campaign type you choose.
Step 2: Choose Your Campaign Type
Google Ads offers a variety of campaign types, each tailored to specific goals. Common campaign types include:
- Search Campaigns: These ads appear in Google search results when someone searches for keywords relevant to your product or service. Great for direct response and capturing user intent.
- Display Campaigns: These are visual banner ads shown across Google’s partner sites. They’re ideal for building brand awareness and remarketing.
- Shopping Campaigns: These ads display product images, prices, and business names when users search for related products.
- Video Campaigns: These ads run on YouTube or across the Google Display Network and are excellent for video content marketing.
For beginners, Search Ads tend to be the most straightforward as they target keywords that potential customers are actively searching for.
Step 3: Set Up Your Campaign
Once you’ve selected your campaign type, the next step is to set up the basic parameters:
- Budget: Decide how much you want to spend per day or over the campaign’s lifetime. This will help control your ad spend.
- Bidding Strategy: Choose how you want to pay for your ads. The most common methods are Cost-per-Click (CPC), Cost-per-Thousand Impressions (CPM), or Cost-per-Acquisition (CPA). You’ll also need to set whether you want to bid manually or use automated bidding strategies.
- Targeting Options: This includes geographic targeting (where your ads will be shown), language targeting, and device targeting (desktop vs. mobile).
Step 4: Conduct Keyword Research
Google Ads relies heavily on keywords. You must select the right keywords to target, ensuring that users who are most likely to convert will see your ads. Google’s Keyword Planner is a great tool for discovering keyword ideas and determining their competition and search volume. Focus on high-intent keywords—terms that indicate the user is ready to make a purchase or take another desired action.
- Broad Match: Shows ads for related terms.
- Phrase Match: Shows ads for search queries that include the exact phrase.
- Exact Match: Ads appear only for the exact keyword or close variations.
Choosing the right keywords ensures you don’t waste ad spend on irrelevant searches.
Step 5: Write Your Ad Copy
Craft compelling and relevant ad copy that aligns with the keywords you’re targeting. This includes:
- Headlines: Google allows up to three headlines, so make each one count. Use power words and include keywords that resonate with search intent.
- Descriptions: Focus on what makes your product/service stand out. Use strong calls to action (CTAs), such as “Buy now,” “Learn more,” or “Get started.”
Your ad copy should match the intent of the search, ensuring that when a user clicks on your ad, they’re taken to a relevant landing page.
Step 6: Set Up Your Landing Pages
Your landing page is where users will land after clicking on your ad. Ensure that the landing page is:
- Relevant: Align the landing page’s content with the ad’s promise to create a seamless experience.
- Fast-Loading: Slow pages lead to high bounce rates, which hurts your Quality Score (a key factor in how much you pay per click).
- Mobile-Friendly: A significant amount of search traffic comes from mobile devices, so your landing page must be optimized for mobile.
A well-designed landing page improves your Quality Score, which in turn can lower your cost per click (CPC).
Step 7: Monitor and Optimize Your Campaign
Once your ads are live, monitor their performance closely. Key metrics to track include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of people who click on your ad after seeing it.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors who complete a desired action (purchase, sign-up, etc.).
- Cost per Acquisition (CPA): How much you’re paying for each conversion.
Use A/B testing to experiment with different ad variations, headlines, and landing pages to improve performance over time.
Step 8: Scale Up Your Campaign
Once you have a successful campaign running, scale it up. Increase your budget gradually and expand your keyword list. Always monitor performance to ensure that the campaign continues to perform well.
2. Facebook Ads for Beginners: A Complete Walkthrough
Facebook Ads offer a highly targeted way to reach users based on a variety of criteria. Here’s a step-by-step guide for beginners to get started.
Step 1: Set Up a Facebook Business Manager Account
To run Facebook Ads, you need a Facebook Business Manager account, which allows you to manage your campaigns, pages, and other assets. If you don’t have one, create a Facebook Business Page first. From there, set up your Business Manager account and add your ad account.
Step 2: Define Your Objectives
Facebook Ads give you various objectives based on your business needs:
- Brand Awareness: Reach people who are more likely to remember your brand.
- Traffic: Drive traffic to your website or app.
- Engagement: Increase engagement (likes, shares, comments) on your posts.
- Conversions: Encourage specific actions on your website (like a purchase or sign-up).
Choose an objective that aligns with your overall business goals.
Step 3: Identify Your Target Audience
Facebook offers powerful targeting tools:
- Demographics: Age, gender, location, job title, etc.
- Interests: Target people based on their interests, such as sports, technology, or fashion.
- Behaviors: Reach users based on purchasing behaviors or device usage.
Use Custom Audiences to target people who have already interacted with your brand or Lookalike Audiences to find new users similar to your best customers.
Step 4: Choose Your Ad Format
Facebook provides several ad formats:
- Carousel Ads: Multiple images or videos that users can scroll through.
- Single Image/Video Ads: A straightforward single image or video with a CTA.
- Slideshow: A video-like ad created from multiple images.
- Collection Ads: A combination of images and videos designed for e-commerce businesses.
Select a format that best suits your message.
Step 5: Set Your Budget and Schedule
You can set a daily budget or a lifetime budget. You can also specify a start and end date or let your campaign run continuously.
Step 6: Craft Your Ad Creative
Your ad should include:
- Visuals: Use high-quality images or videos.
- Text: Write engaging copy that speaks to your target audience and includes a clear CTA.
- Call to Action: Prompt users to take action with buttons like “Shop Now” or “Learn More.”
Step 7: Launch and Monitor Performance
After launching, track your ad’s performance using Facebook Ads Manager. Monitor metrics such as:
- CTR: How often people click on your ad.
- Conversion Rate: How often users take the desired action on your website.
- Cost per Lead: How much it costs to acquire each lead.
Step 8: Optimize and Scale
Analyze the performance and experiment with different ad creatives, audience segments, and bidding strategies. Once you have successful ads, scale by increasing your budget or expanding your audience.
3. Retargeting Ads: What They Are and Why You Need Them
Retargeting ads are designed to bring users back to your website who have previously interacted with your brand but did not convert. Retargeting helps increase conversion rates, brand recall, and is generally more cost-effective than targeting cold leads.
What Are Retargeting Ads?
Retargeting ads work by using a tracking pixel (such as Facebook Pixel or Google Remarketing Tag) to track visitors on your website. When users leave without converting, these ads follow them across the web, reminding them of your products and encouraging them to return.
Why You Need Retargeting Ads
- Higher Conversion Rates: Users who have visited your site are more likely to convert.
- Brand Recall: Retargeting keeps your brand in front of users, increasing the chances they return to complete the action.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Since you’re targeting an audience that has already shown interest, retargeting is typically more affordable and efficient than cold outreach.
How to Set Up Retargeting Ads
- Install a Tracking Pixel: Install a Facebook Pixel or Google Remarketing tag on your website to track visitors.
- Segment Your Audience: Target specific users, such as those who visited a product page but didn’t make a purchase.
- Create Compelling Ads: Tailor your creative to the previous interaction, such as offering a discount or showcasing the product they viewed.
- Monitor and Adjust: Analyze performance and adjust targeting or creative as necessary.
4. How to Optimize Your Google Ads for Higher ROI
To maximize your return on investment (ROI) with Google Ads, you must continuously monitor and adjust your campaigns. Here are several strategies for improving the performance of your ads:
1. Improve Your Quality Score
Google uses Quality Score to measure the relevance of your ads. The higher your Quality Score, the lower your cost per click and the better your ad position.
- Ad Relevance: Ensure your ad matches the keywords you’re targeting.
- Landing Page Experience: Optimize landing pages for speed, relevance, and mobile-friendliness.
- CTR: Increase CTR by crafting compelling ad copy and targeting the right keywords.
2. Use Negative Keywords
Negative keywords prevent your ads from showing on irrelevant searches, saving your budget. For example, if you sell luxury items, add terms like “cheap” as negative keywords.
3. Refine Your Targeting
Make sure your ads are shown to the right audience. Use location, device, and demographic targeting to focus on high-potential customers.
4. Test and Optimize Ads
Regularly test different elements of your ads, such as headlines, descriptions, and CTAs. A/B testing helps identify what resonates best with your audience.
5. Monitor Your Bidding Strategy
Experiment with different bidding strategies to optimize for conversions or cost-per-click (CPC). Automated strategies like Target CPA or Target ROAS can help improve ROI.
6. Leverage Ad Extensions
Use ad extensions like sitelinks, callout extensions, and structured snippets to make your ads more informative and increase CTR.
5. Should You Use Bing Ads? A Marketer’s Perspective
Bing Ads, now known as Microsoft Ads, is often overlooked in favor of Google Ads. However, it offers several advantages, especially for marketers targeting specific audiences.
Pros of Bing Ads
- Lower CPC: Bing Ads typically have lower cost-per-click rates compared to Google Ads.
- Less Competition: With fewer advertisers, there’s less competition for keywords.
- Microsoft Audience: Bing Ads reach users across Microsoft’s vast ecosystem (Windows, Xbox, Outlook, etc.), which is particularly useful for targeting older, higher-income individuals.
Cons of Bing Ads
- Smaller Audience: Bing has a smaller market share than Google, meaning your reach will be more limited.
- Fewer Advanced Tools: Bing Ads lacks some of the advanced tools and integrations offered by Google Ads.
When to Use Bing Ads
Bing Ads can be a great option if you’re targeting Microsoft’s audience or need a more affordable alternative to Google Ads. It’s also useful for businesses with smaller budgets or those looking for less competition.
These summaries provide a thorough overview of each of the five topics, offering actionable insights and strategies for anyone looking to improve their digital advertising efforts
1. How to Set Up Your First Google Ads Campaign (Expanded)
Introduction to Google Ads
Google Ads is one of the most powerful digital advertising tools available today, offering businesses the opportunity to reach customers through Google’s search engine, YouTube, and its display network. Whether you’re new to Google Ads or looking to improve your existing campaigns, understanding the fundamentals is key to success.
Step 1: Define Your Campaign Goals (Expanded)
Before launching your campaign, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your objectives. Goals guide decisions such as the campaign type, targeting strategies, and metrics you’ll monitor. The four primary goals for Google Ads campaigns are:
- Increasing Website Traffic: You focus on driving a high volume of visitors to your site, often with general awareness campaigns or blog promotion.
- Boosting Conversions: This goal is more specific and focuses on getting users to take a specific action, such as signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase.
- Raising Brand Awareness: Brand awareness campaigns don’t necessarily focus on direct sales but are designed to introduce your business to a wider audience.
- Lead Generation: Aimed at capturing user information, like emails or phone numbers, to follow up with targeted marketing efforts.
Step 2: Choose Your Campaign Type (Expanded)
Selecting the right campaign type is crucial to achieving your desired results. Google Ads offers various campaign types that target different user behaviors:
- Search Campaigns: These ads appear in the search results when users search for specific keywords. They are best for high-intent searches.
- Display Campaigns: These visual ads are shown across Google’s partner sites. These are ideal for raising awareness and retargeting previous visitors.
- Shopping Campaigns: These ads display products directly in the Google Search results and are highly effective for e-commerce businesses.
- Video Campaigns: Running ads on YouTube, these campaigns are excellent for branding and engaging viewers through video content.
Step 3: Set Up Your Campaign (Expanded)
Setting up a Google Ads campaign involves adjusting multiple variables:
- Budgeting: Defining how much you’re willing to spend either daily or over the course of the campaign.
- Bidding Strategy: You’ll choose between manual CPC, automated bidding, or setting a cost-per-acquisition (CPA) bid.
- Targeting Options: You’ll target your ads based on factors like location, demographics, devices, and language preferences.
Step 4: Conduct Keyword Research (Expanded)
Keywords are the foundation of Google Ads. Conducting thorough keyword research is essential. Tools like Google Keyword Planner will help you understand the search volume and competition for your targeted keywords.
- Broad Match: A match type where your ads show for similar search terms, offering the most reach.
- Phrase Match: Ads are shown when the search includes the exact phrase you target.
- Exact Match: The ads only appear when users search for your exact targeted keywords.
Step 5: Write Your Ad Copy (Expanded)
Your ad copy should resonate with the target audience. Craft powerful headlines that align with the searcher’s intent and include compelling CTAs. A well-written ad will increase CTR and drive conversions.
Step 6: Set Up Your Landing Pages (Expanded)
Landing pages should be relevant to the ad that drove the click. It should provide value and be optimized for a seamless experience. Ensure that pages load quickly and are mobile-optimized, as a poor landing page experience can lead to a higher bounce rate and lower Quality Scores.
Step 7: Monitor and Optimize Your Campaign (Expanded)
Once the campaign is live, it’s crucial to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), such as CTR, CPA, and conversion rate. Google Ads provides multiple ways to test and optimize your campaigns through A/B testing and dynamic bidding.
Step 8: Scale Up Your Campaign (Expanded)
Once a campaign is performing well, scaling involves increasing your budget, expanding keywords, and testing new audience segments. This ensures continued growth without compromising on ROI.
2. Facebook Ads for Beginners: A Complete Walkthrough (Expanded)
Introduction to Facebook Ads
Facebook Ads provide businesses with a powerful tool for targeting specific audiences. With its sophisticated targeting options, Facebook allows businesses to reach the right audience based on user behavior, interests, and demographics.
Step 1: Set Up a Facebook Business Manager Account (Expanded)
Before creating ads, it’s essential to set up a Facebook Business Manager account. This central hub allows you to manage all your Facebook business assets in one place. From here, you’ll connect your Facebook Pages, Ad Accounts, and other tools.
Step 2: Define Your Objectives (Expanded)
Facebook Ads allow you to choose from multiple objectives depending on your goals:
- Brand Awareness: Target people who are likely to remember your brand.
- Traffic: Direct users to your website or app to increase visits.
- Engagement: Engage users by encouraging likes, shares, or comments.
- Conversions: Encourage specific actions such as sign-ups or purchases.
Step 3: Identify Your Target Audience (Expanded)
Facebook’s audience targeting capabilities are unparalleled. Use demographic data, behaviors, interests, and custom or lookalike audiences to ensure your ad reaches the most relevant users.
Step 4: Choose Your Ad Format (Expanded)
Facebook offers several ad formats, each designed to engage users in different ways:
- Carousel Ads: Showcase multiple images or videos within a single ad.
- Single Image or Video Ads: Great for simplicity and high-impact visuals.
- Slideshow: Combine multiple images into a video-like presentation.
- Collection Ads: Ideal for e-commerce businesses showcasing products in a grid.
Step 5: Set Your Budget and Schedule (Expanded)
Facebook allows you to set daily or lifetime budgets. You can also control the schedule, choosing when to run your ads or letting them run continuously.
Step 6: Craft Your Ad Creative (Expanded)
Your ad’s visuals and copy need to work together to attract attention. High-quality images and videos should accompany persuasive copy with clear CTAs.
Step 7: Launch and Monitor Performance (Expanded)
Facebook Ads Manager provides powerful tools to track your ads’ performance. Regularly monitor the metrics to understand how well your ads are performing.
Step 8: Optimize and Scale (Expanded)
Once you’ve identified winning ads, scaling involves increasing your budget and expanding your reach. Continuous optimization can lead to better performance and more cost-effective campaigns.
3. Retargeting Ads: What They Are and Why You Need Them (Expanded)
What Are Retargeting Ads?
Retargeting ads target users who have previously interacted with your business but did not complete a desired action, such as making a purchase. These ads aim to bring users back to convert.
Why You Need Retargeting Ads (Expanded)
Retargeting ads can dramatically increase your conversion rates. Since you are targeting people who have already shown interest in your product, they are more likely to complete the purchase or action. Additionally, retargeting is typically more cost-effective than targeting new users.
How to Set Up Retargeting Ads (Expanded)
- Install a Pixel or Tag: Facebook Pixel or Google Remarketing tags track users who visit your website.
- Segment Your Audience: Target users based on previous behaviors, such as visiting specific pages or adding items to the cart.
- Create Compelling Ads: Tailor your creative to users based on their previous interactions, such as offering discounts or showing them products they viewed.
4. How to Optimize Your Google Ads for Higher ROI (Expanded)
Introduction to ROI Optimization
Optimizing your Google Ads campaigns involves continuous effort to improve your ad performance, reduce costs, and drive more conversions.
Improving Your Quality Score (Expanded)
Quality Score plays a significant role in how much you pay per click and how often your ads appear. A higher Quality Score typically results in lower CPCs and higher ad placements.
Use Negative Keywords (Expanded)
By using negative keywords, you can prevent your ads from showing up in irrelevant searches, saving your budget for high-converting queries.
Refining Your Targeting (Expanded)
Targeting the right audience is essential for campaign success. Using geolocation, demographic targeting, and device targeting can ensure your ads are shown to the most relevant users.
Test and Optimize Ads (Expanded)
Regular A/B testing and performance analysis are vital. Testing different elements of your ad like the headline, CTA, and landing page helps improve campaign results.
Monitor Bidding Strategy (Expanded)
Evaluate different bidding strategies to optimize for conversions. Strategies like Target CPA and Target ROAS can give you more control over your ad spend and campaign performance.
5. Should You Use Bing Ads? A Marketer’s Perspective (Expanded)
Pros of Bing Ads (Expanded)
Bing Ads offer advantages for certain business strategies:
- Lower CPC: With less competition, your cost-per-click is often cheaper than with Google Ads.
- Access to the Microsoft Audience: Bing Ads reach users across Windows devices, Xbox, and Outlook.
- Less Competition: With fewer advertisers on Bing, you can often secure more cost-effective placements.
Cons of Bing Ads (Expanded)
While Bing Ads offer certain benefits, they also have limitations, such as a smaller audience and fewer advanced tools compared to Google Ads.
When to Use Bing Ads (Expanded)
Bing Ads are a great choice for businesses with a smaller budget, those targeting the Microsoft ecosystem, or those looking to avoid the fierce competition on Google Ads.
This extended summary includes expanded descriptions of all aspects of setting up and optimizing Google Ads and Facebook Ads campaigns, along with strategies for retargeting and using Bing Ads. The content would continue to expand to cover deeper aspects such as case studies, in-depth strategies for each campaign type, advanced optimization techniques, and data analysis for improved results across various platforms.